|
|
ELECTRODIALYSIS |
MENU
|
ELECTRO- DIALYSIS |
||
|
ION-EXCHANGE MEMBRANE An ion-exchange membrane (IEM) is a membrane that
allows certain ions to pass through, but prevents
transport of other ions or neutral molecules. A CATION-EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (CEM) is permeable to
cations. CEMs are commonly formed of polymers with negatively charged functional
groups. An ANION-EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (AEM) is permeable to
anions. AEMs are commonly formed of polymers with positively charged
functional groups. |
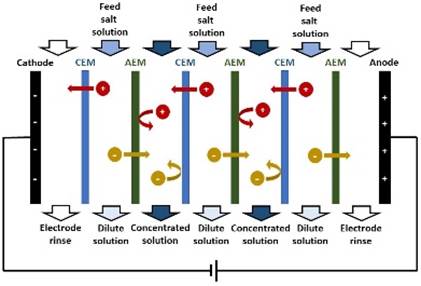
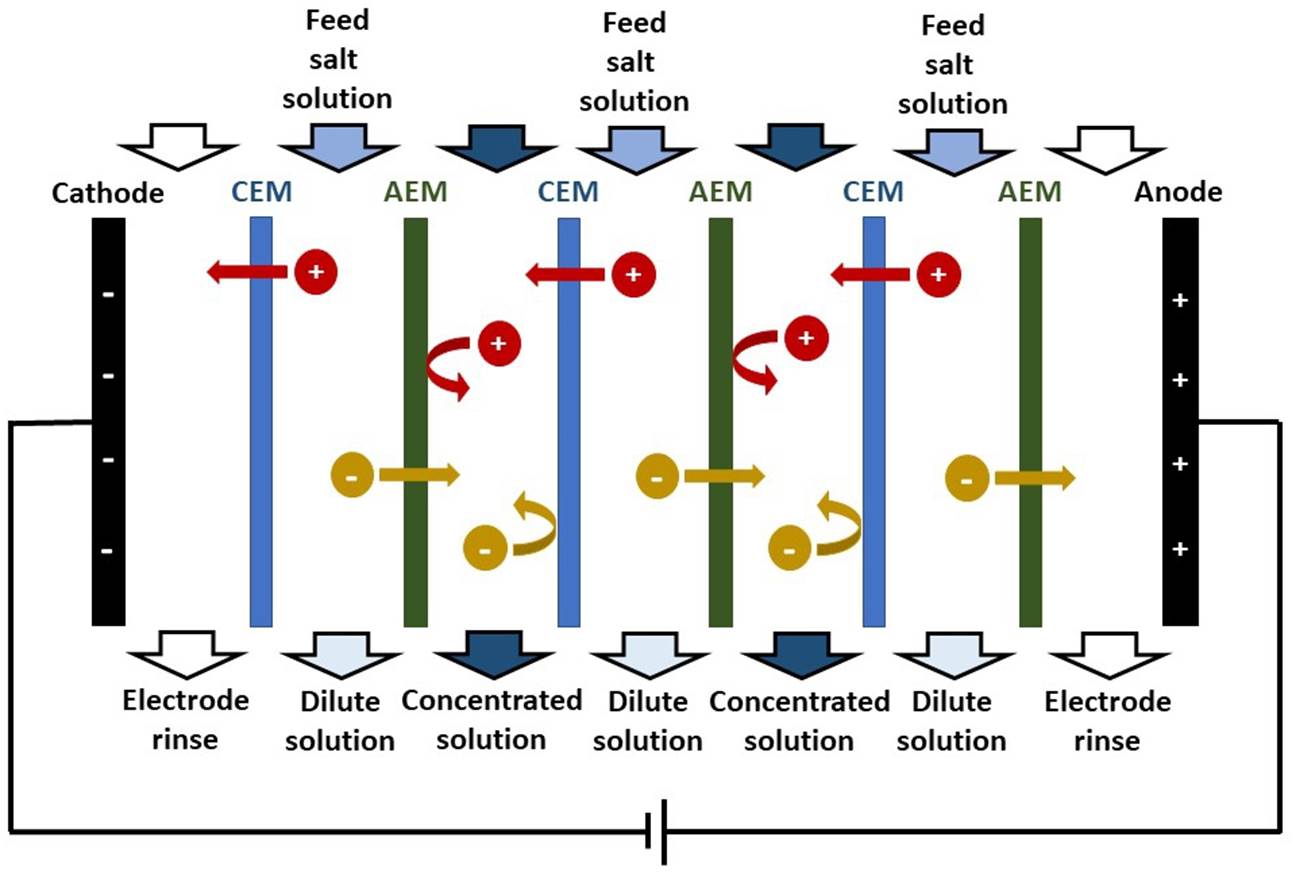
ELECTRODIALYSIS In electrodialysis, an applied electric potential
difference is used to transport salt ions through ion-exchange membranes from
one solution to another. An ELECTRODIALYSIS STACK consists of a series of CEMs
and AEMs (separating dilute and concentrated solution streams) between two
electrodes. |
|
|
|
|
DESALINATION ELECTRODIALYSIS may be used to remove salt from
brackish water or seawater, as well as for a variety of other applications. In electrodialysis the ions are removed from the
feed water stream, unlike processes such as reverse osmosis (RO) where the
water is removed. Electrodialysis is generally more cost-effective
for feeds with low salt concentration and RO for feeds with higher salt concentration. |
|
|
|
|