|
|
MEMBRANE POLYMERS |
MENU
|
MEMBRANE POLYMERS |
||
|
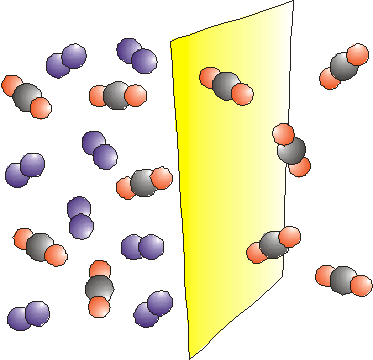
Many synthetic membranes are made of polymers. A polymer is composed of giant molecules
(macromolecules) consisting of repeating units. |
|
|
|
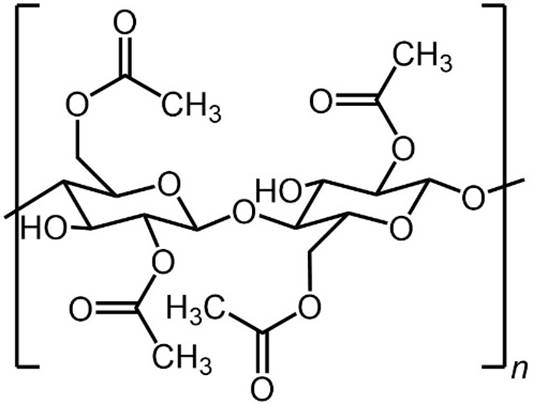
CELLULOSE
ACETATE Cellulose acetate is a
chemically modified natural polymer. Cellulose is obtained from wood
and green plants. The acetate ester of
cellulose was first prepared in 1865. Cellulose acetate is used in membranes for reverse osmosis (seawater
desalination) and gas separation (CO2 removal from natural gas). |
|
POLYSULFONE Polyarylethersulfone (often just called “polysulfone”) is a
glassy synthetic polymer. Polysulfone is used in membranes for gas separation (hydrogen recovery
in ammonia production). |
|
|
|
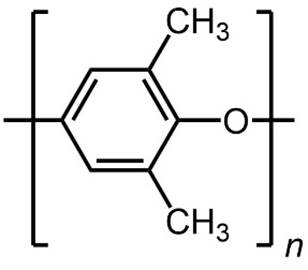
POLYPHENYLENE OXIDE Polyphenylene oxide is a glassy synthetic polymer. Polyphenylene oxide is used in
membranes for gas separation (air separation for generating nitrogen). |
|
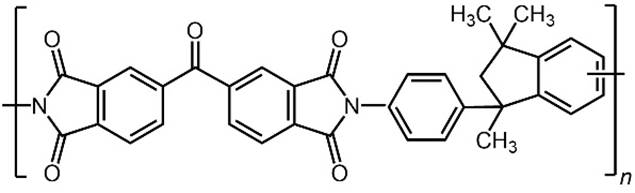
POLYIMIDES Aromatic polyimides are thermally-stable, glassy synthetic polymers. A commercial example of a
polyimide is Matrimid 5218. Polyimides are
used in membranes for gas separation (air separation for generating
nitrogen). |
|
|
|
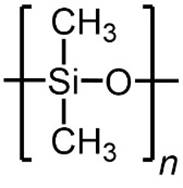
SILICONE Silicone rubbers include
polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). PDMS is used
in membranes for pervaporation (recovery of alcohols from aqueous mixtures). |
|
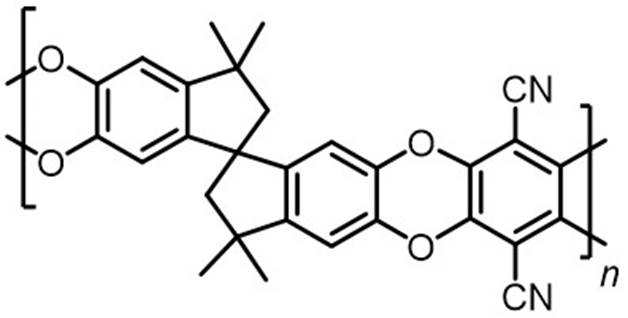
POLYMERS OF INTRINSIC MICROPOROSITY Polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIMs) are glassy polymers
with rigid, contorted macromolecular backbones that cannot fill space efficiciently. Their high free volume gives them high
permeability to gases. The prototypical example of a PIM is referred
to as PIM-1. |
|