ML2921: Tissue Interactions and Biocompatibility
Cell and tissue damage
Necrosis
- Coagulation necrosis
- Most common
- Acidophilic opaque "tombstone"
- Loss of nucleus but preservation of basic cell shape
- Occurs commonly from sudden severe ischemia
- Denaturation of structural and enzymic proteins therefore preventing proteolysis of the cell
- Kidney, heart
- Liquefaction necrosis
- Results from action of powerful hydrolytic enzymes
- Ischemic destruction of brain tissue, bacterial lesions
- Fat necrosis
- Due to action of lipases in adipose tissue
- Pancreatic necrosis
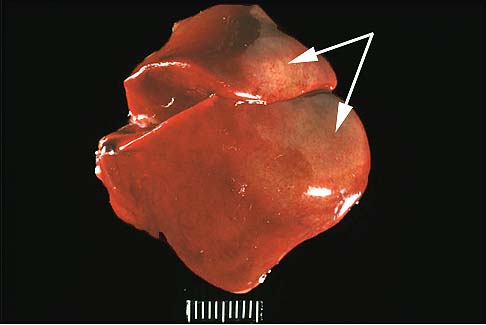
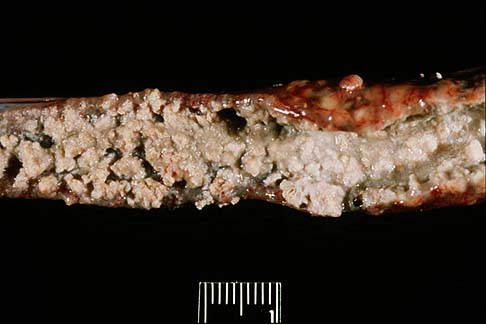
- Caseous necrosis
- Combination of coagulative and liquefactive
- Tuberculous infections
- Enclosed within granulomatous inflammatory wall
- Gangrenous necrosis
- Generally lower leg
- Loss of blood supply leads to bacterial infection
- Tissue has undergone ischemic cell death
- Coagulative necrosis is modified by liquefactive action of the bacteria and the attracted leucocytes
- Coagulative dominant = dry gangrene
- Liquefactive dominant = wet gangrene


| Prev | Back to beginning |
Useful Links:
Lectures:
- Year 1:
- The Cell
- Biochemistry
- Year 2:
- Tissue Interactions and Biocompatibility
- Year 3/4:
- Tissue Engineering
- Biosensors