Pathogens 2: Bacteria
Intracellular Bacteria
In absence of opsonins, macrophages can engulf bacteria and become infected
Bacteria must therefore have survival strategies
- Avoid phagosome maturation
- Escape from phagosome into cytoplasm
- Release enzymes that lyse the phagosome membrane
- Inhibit fusion with lysosomes
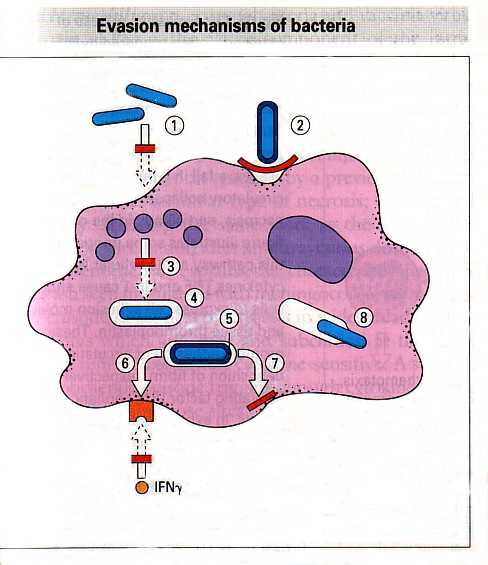
- Secrete repellents or toxins inhibiting chemotaxis
- Have capsules or outer coats which inhibit phagocyte attachment
- Allow uptake but release factors that block killing mechanisms
- Secrete catalase which inhibits hydrogen peroxide
- M.Leprae for example has highly resistant outer coat, phenolic glycolipid which scavenges free radicals
- Mycobacteria release lipoaribinomannan - blocks macrophages responding to IFN
- Stop antigen presentation
- Escape phagosome to multiply in cytoplasm
| Prev | Back to beginning |
Useful Links:
Lectures:
- Year 1:
- Cell Biology
- Year 2:
- Tissue Interactions and Biocompatibility
- Year 3/4:
- Tissue Engineering