Wrist Analysis in radiographs
Segmenting Overlapping Bones
Many shape matching techniques use a single shape model, together with one local model for each model point which assumes that the appearance around each point is either independent of that around its neighbors or linearly related. This assumption is broken when two bones are superimposed.

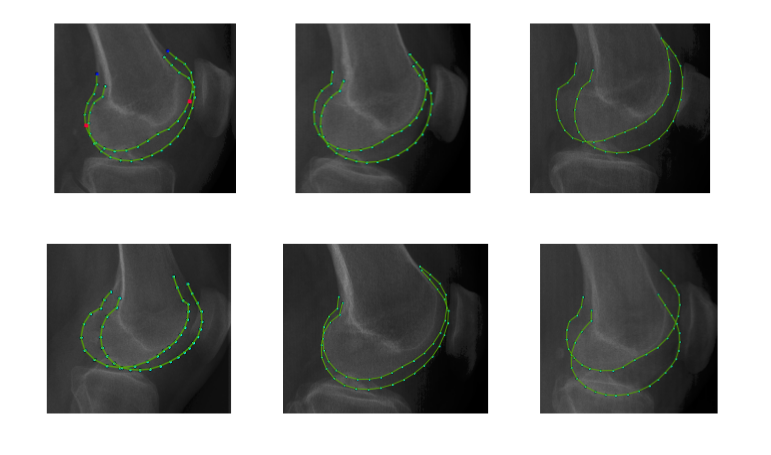
- These are some examples of different relative positions the radius and the ulna can take in clinical lateral wrist radiographs.
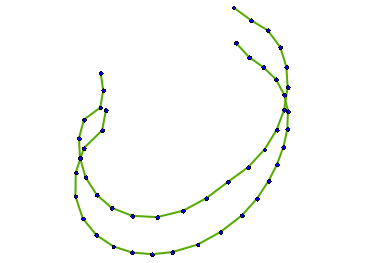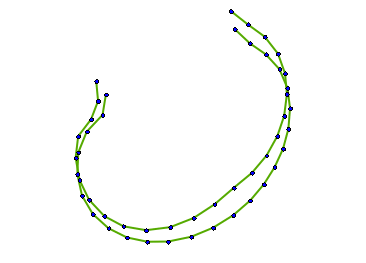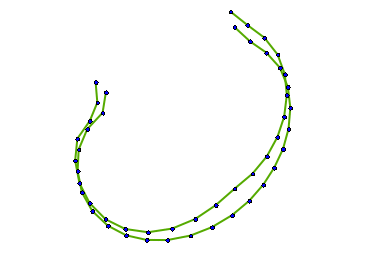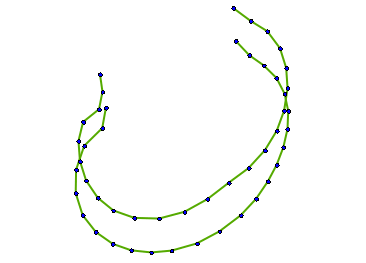
- The moving images below show the 3 highest patterns of variation in the dataset.

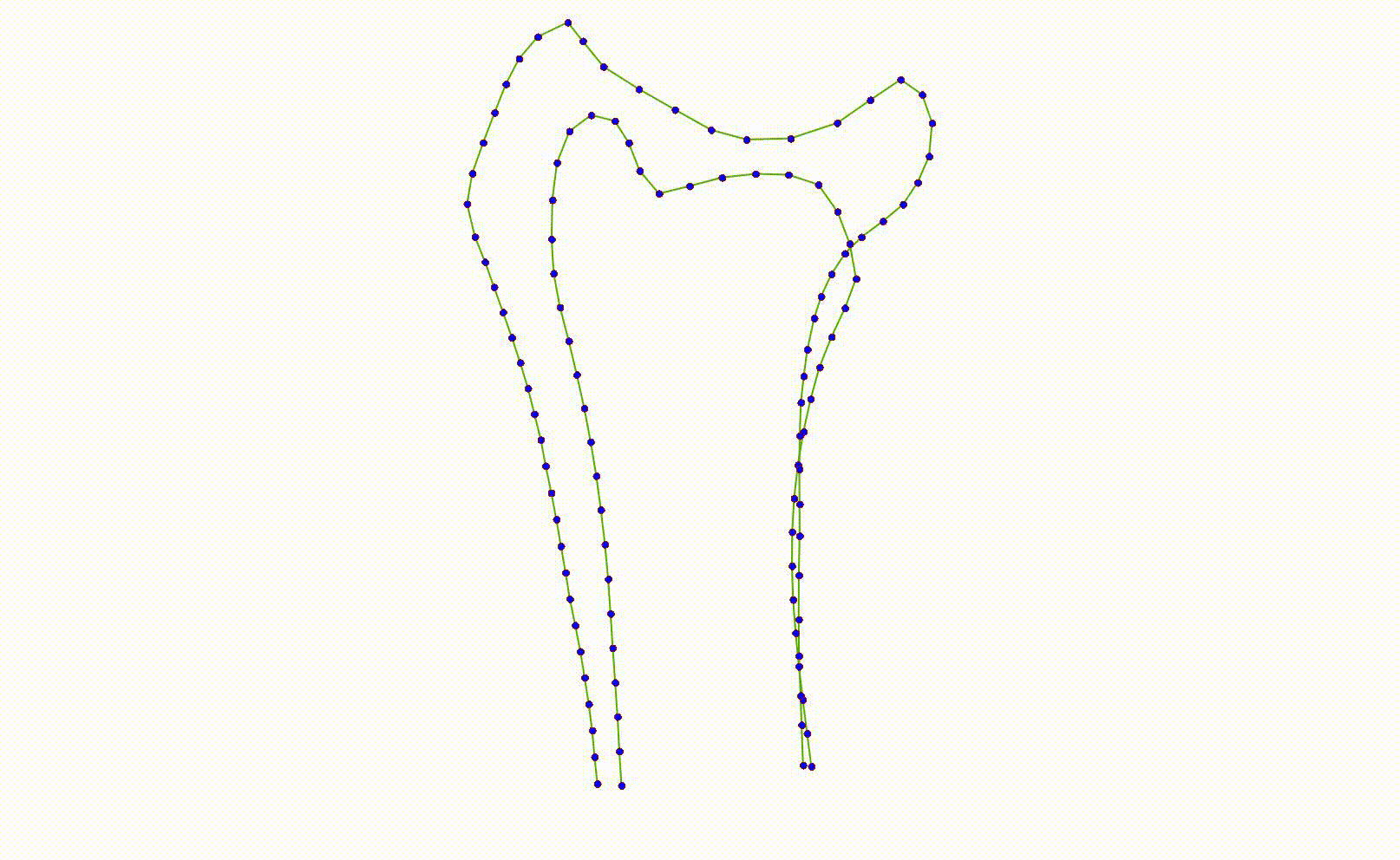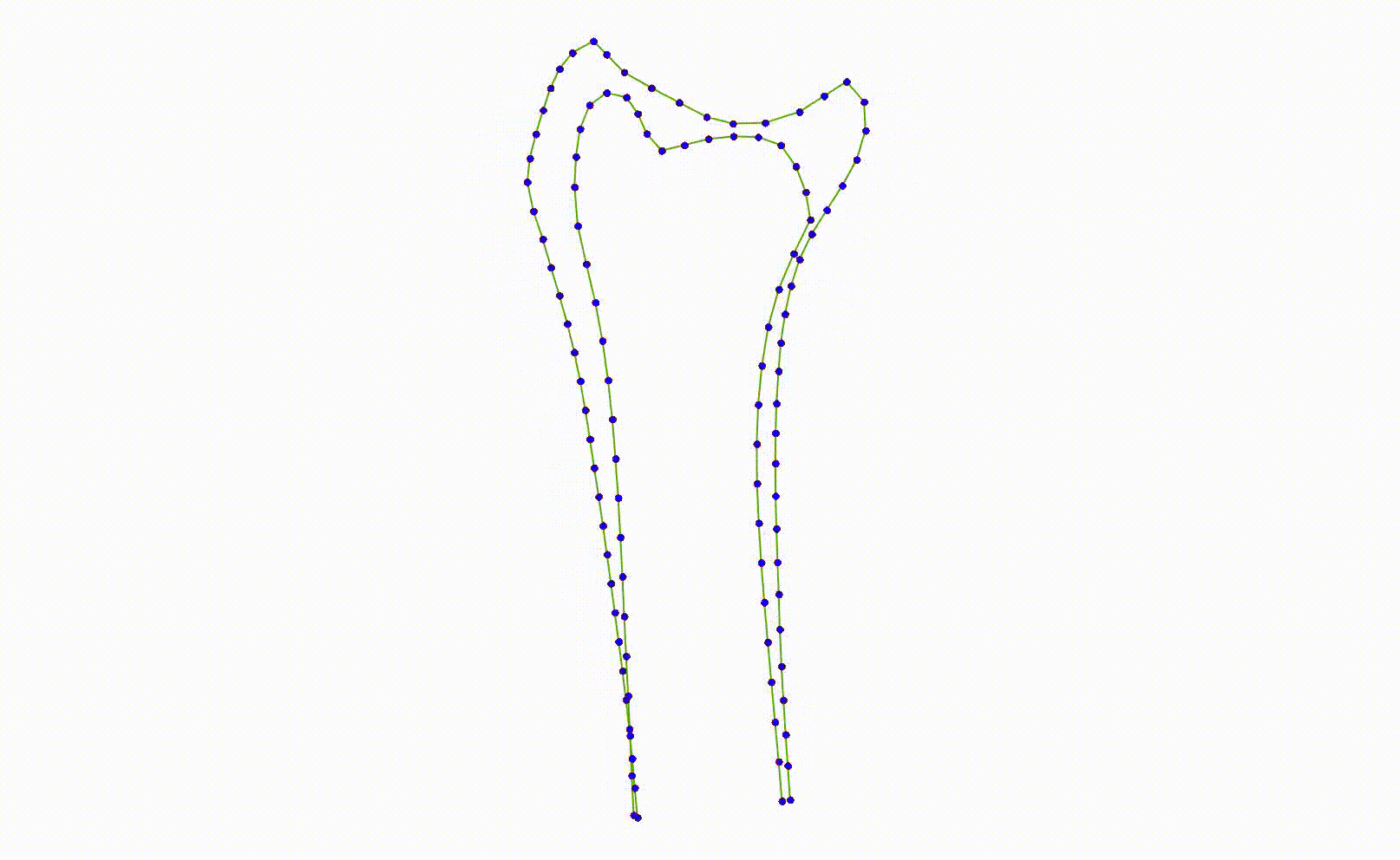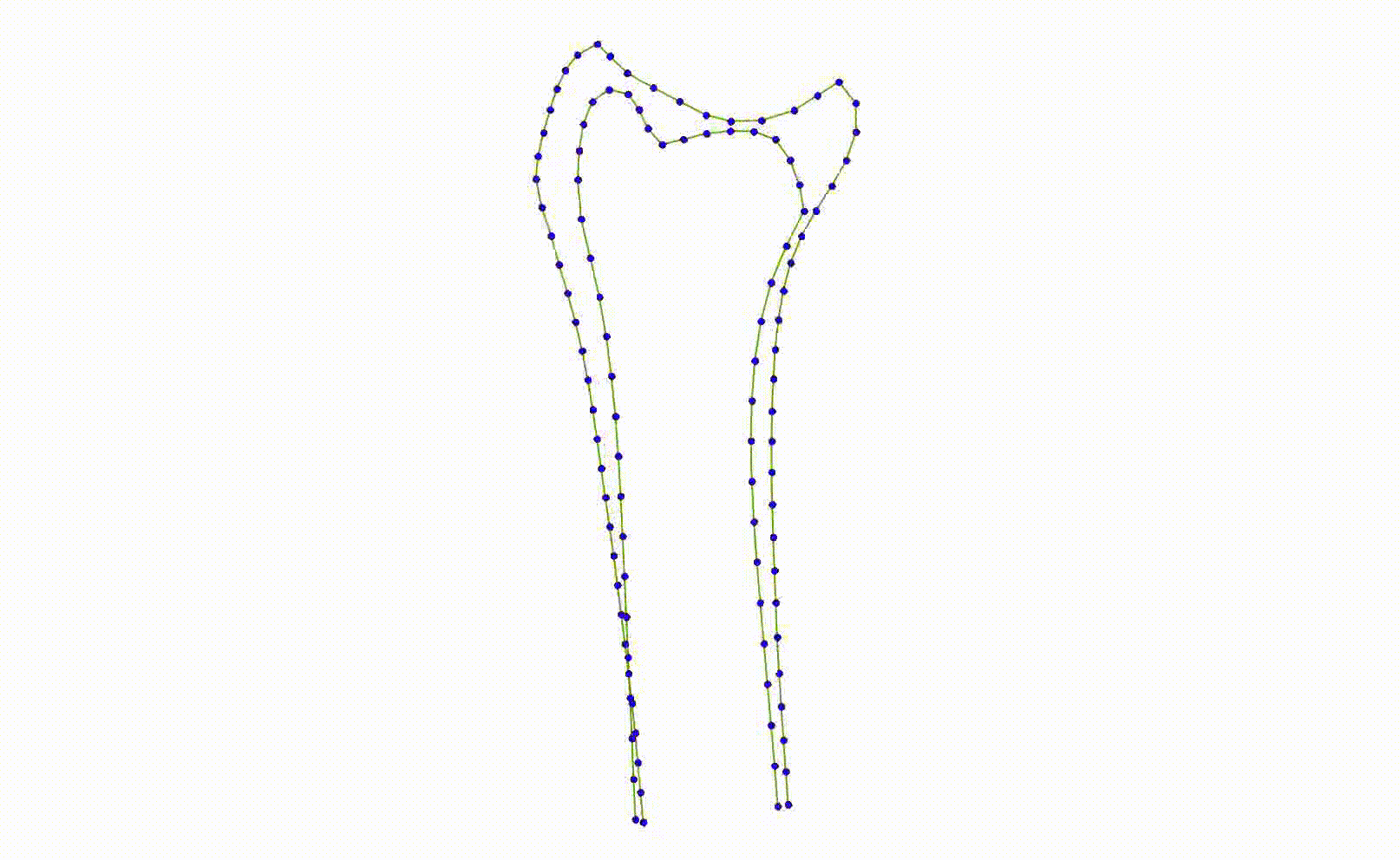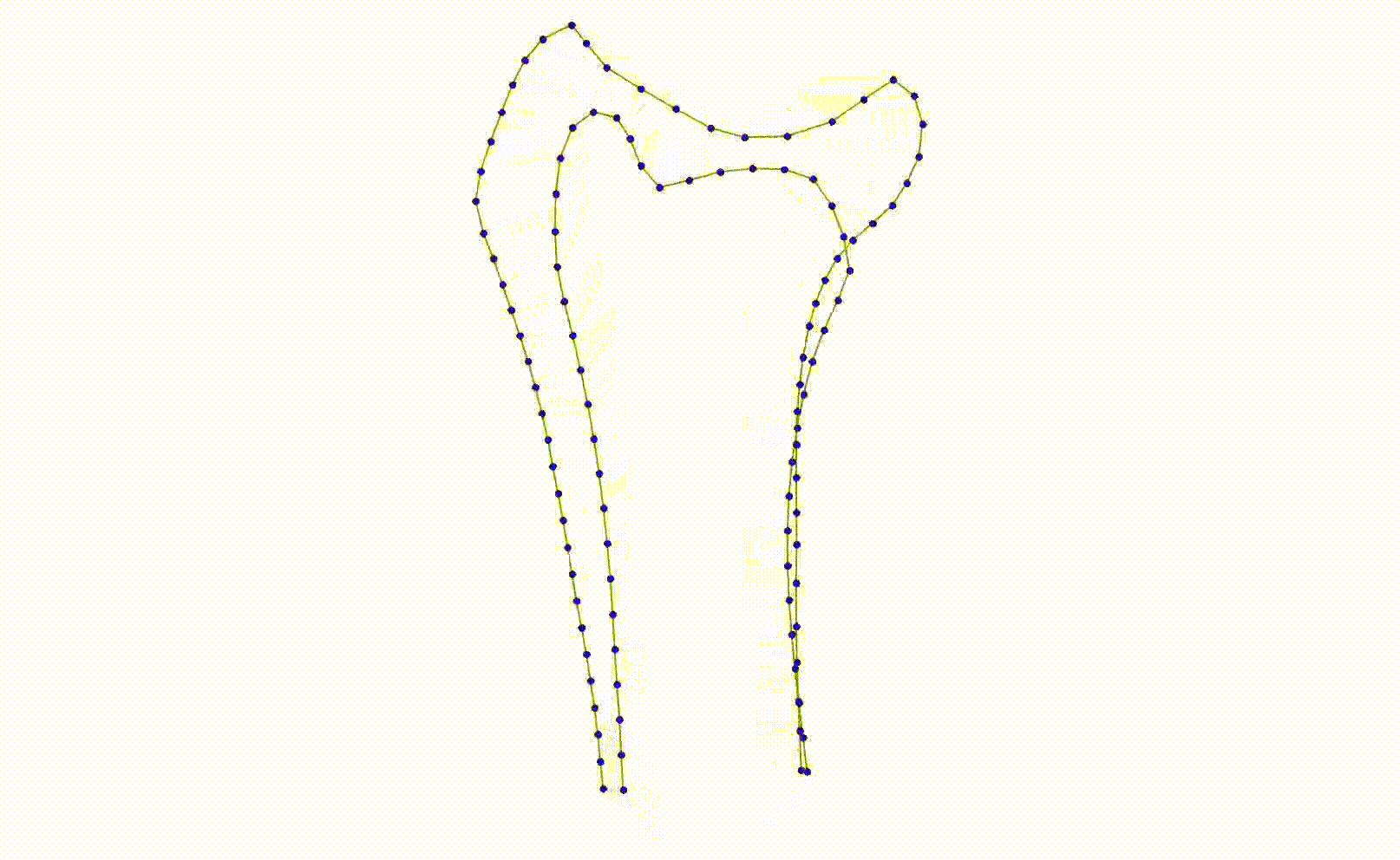

- A local model trained on examples where the ulna is to the left will not work well when it is to the right, and vice-versa.
- To overcome this limitation we proposed work on improving the state-of-art technique Random Forest
Regression Voting Constrained Local Model (RFRV-CLM) in order to perform better on overlapping structures in lateral radiographs by:
- Building different sets of local models.
- Each set corresponds to a certain alignment of the overlapping bones and contains one local model per model point.
- The proposed fitting algorithm switches between these sets depending on the global shape (i.e. current positioning).
- Results showed significant improvements in accuracy and robustness when segmenting
(i) the radius and ulna in radiographs of the wrist, and (ii) femoral condyles in lateral
knee radiographs.