MATH35001 Viscous Fluid Flow: Flow through a porous channel
with constant transverse velocity
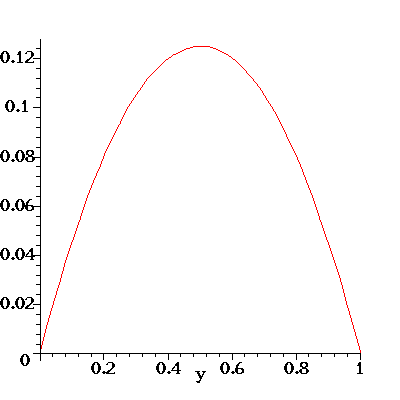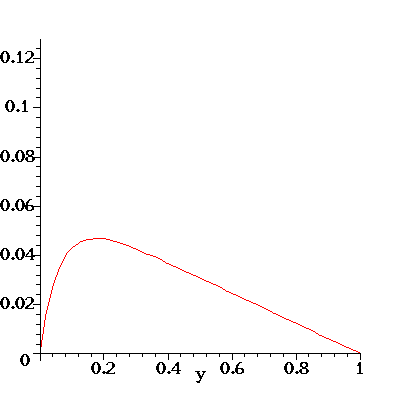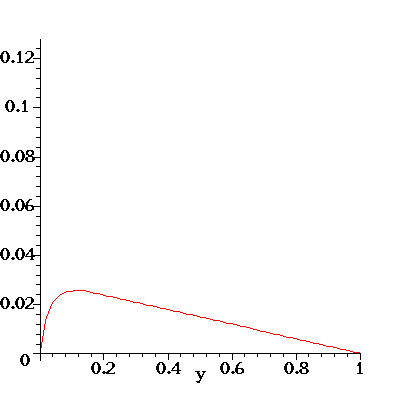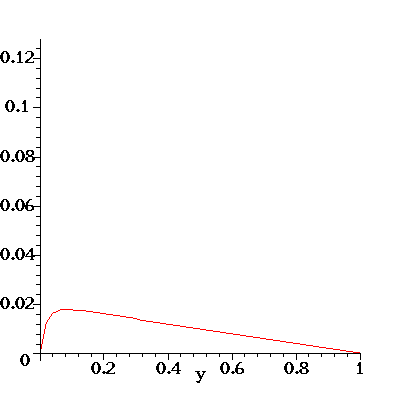
Here's an illustration of the flow profile u(y) for the flow in a
channel with porous walls. The flow is driven
by an axial pressure gradient dp/dx = G. Fluid enters (and leaves)
the channel through the porous walls which are located at y=0
and y=1 and the fluid has a constant transverse velocity v=-V.
The flow profile is governed by the equation
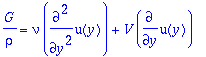
For the animation below I have set rho=-G=mu=1. As the animation progresses,
the transverse velocity V is increased from 0 to 50 (in equal steps).
Note how this skews the initially symmetric (and parabolic) velocity
profile. The pressure gradient G is kept constant and the increased
viscous dissipation due to the large wall shear stress at the bottom
wall (look at the velocity gradient at y=0!) reduces the overall flow rate
through the channel as V increases.
Page last modified: October 26, 2007
Back to Matthias Heil's home page..